0x00 学习过程
根据慕课网Spring Security开发安全的REST服务
说实话,我觉得不值366这个价,当然我看的盗版,但是像极客时间一样99元还可以接受
我推荐不用看视频,毕竟光半懂不懂听完就要20几个小时,还不包括跟着写代码和调试的时候遇到问题解决,还有自己回顾和理解源码,从上班人的角度讲太耗时间了,从课程作者的代码来学习,根据branches的小节,从小到大一节节代码比对来看效果更好,挑几个版本分析一下源码,最后再看一下讲源码的部分
作者是STS来写的,我用IDEA,然后把文件上传、多线程和WireMock这些和主线无关的功能去去掉,重新写了一遍
其实这门课实现的是一个RBAC访问控制系统,但是认证方式多了短信、SSO、OAuth2等很多种,可能也讲究怎么设计才能更好复用
RABC大学时候就学过,学Web的时候用Python写一个也很快
实际上用Spring+Spring Security实现比Python的Flask实现,就因为Java语言和Spring本身的特性,多了很多绕弯子的知识点
什么IoC、AOP、Filter、Interceptor这些,还有各类注解,感觉就是将自定义类和类关系的过程变成了理解注解的过程,我觉得更复杂了,比起一个Flask的装饰器和顾名思义的before_request这样的函数差太多了,至少觉得如果我几年前一开始学RBAC是用Java学的话,肯定被绕进Java和Spring里面去,而不是学RBAC模型
不过,本身我也就是为了学习框架而已,至于实现,好像知道Java的Servlet,知道Spring Security是用Filter实现的,剩下的就都是细节了
感觉上就是像Flask一样的框架把原理都给你说了,需要什么功能自己加,Spring这种就是什么东西都有了,需要什么功能自己学着用,所以学起来特别复杂,重要都是光会用不清晰就朦朦胧胧,不知道学多久能了然于胸,不慌不忙
0x01 简单Restful接口学习和实现
这部分代码可以看3-11版本
这里有几个知识点
- Swagger生成文档:看一下就明白了
- REST服务增删改查接口:写几个接口就知道了
- Validate使用和自定义:搜索下各个注解的意思,自定义和原生注解实现比对
- Filter、Interceptor和切片拦截REST服务:三种拦截的方式,Filter学过Servlet本来就知道,Interceptor和切片是Spring的东西,看看三者的拦截情况
访问http://127.0.0.1:8060/user/1查看日志输出,尤其留意Filter、Interceptor和切片拦截的流程,这个部分基本就可以了
0x02 Spring Security开发基于表单的登录及认证过程原理分析
这部分代码可以看4-06版本
思路
这个例子比较简单,其实是理解Spring Security的Config配置的代码和对应需要自己写的一些实现类,去掉作者的模块划分和设计模式的话
@Configuration
public class BrowserSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
// 省略
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/authentication/require")
.loginProcessingUrl("/authentication/form")
.successHandler(authenticationSuccessHandler).failureHandler(authenticationFailureHandler)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/authentication/require", securityProperties.getBrowser().getLoginPage()).permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and().csrf().disable();
}
}
真的,看到配置代码里有and()这种函数就惊呆了,毕竟也不是ORM,从配置代码来看就是默认情况使用Spring Security是使用HTTP Basic Auth,配置中改成自定义表单
指定登录路由/authentication/require
@RestController
public class BrowserSecurityController {
// 省略
@RequestMapping("/authentication/require")
@ResponseStatus(code = HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED)
public SimpleResponse requireAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
SavedRequest savedRequest = requestCache.getRequest(request, response);
if (savedRequest != null) {
String targetUrl = savedRequest.getRedirectUrl();
logger.info("引发跳转的请求是:"+targetUrl);
if(StringUtils.endsWithIgnoreCase(targetUrl, ".html")){
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, securityProperties.getBrowser().getLoginPage());
}
}
return new SimpleResponse("访问的服务需要身份认证,请引导用户到登录页");
}
}
登录路由的内容是如果请求的是html页面就用LoginPage,也就是自定义的html页面,输入用户名密码后的验证接口是/authentication/form
配置验证函数在MyUserDetailsService继承UserDetailsService,根据业务自己写,实现的UserDetails和User需要知道参数含义
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
// 省略
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
logger.info("登录用户名:" + username);
String password = passwordEncoder.encode("123456");
logger.info("数据库密码是:" + password);
return new User(username, password, true, true, true, true,
AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin"));
}
}
验证成功和失败后的处理,这里以成功为例子,可以根据JSON或者其他类型进行修改返回,继承SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler是继承登录成功后跳转,其实这部分不写也没关系,但是课程里写了就试了
@Component("AuthenticationSuccessHandler")
public class AuthenticationSuccessHandler extends SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler {
// 省略
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws ServletException, IOException {
logger.info("登录成功");
if (LoginType.JSON.equals(securityProperties.getBrowser().getLoginType())) {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(authentication));
} else {
super.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authentication);
}
}
}
基本上这样代码流程就完成了,之后添加图形验证码和手机验证码的功能其实没什么必要学
认证过程流程分析
其实我觉得Debug找入口是最困难的,本来写得代码就是继承类和一些配置代码
课程里分析的过滤器的执行顺序我觉得还是不清晰,还是网上找了很多文章看
分析程序从数据结果和算法来
第一个数据结构,也就是认证信息,也可以理解为用户认证信息
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
// 权限集合 AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin")) 返回字符串权限集合
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
// 因为调试是null没有调试出来什么意思,大概是认证过程的敏感信息
Object getCredentials();
// 认证时的一些信息
Object getDetails();
// 认证策略
Object getPrincipal();
// 是否被认证
boolean isAuthenticated();
void setAuthenticated(boolean var1) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
一个Authentication对象的内容,可以帮助清晰理解
authorities: [{authority: "admin"}]
details: {remoteAddress: "127.0.0.1", sessionId: "377F06C5652B56D91F08C9167CDE40A5"}
authenticated: true
principal: {password: null, username: "123", authorities: [{authority: "admin"}], accountNonExpired: true, accountNonLocked: true, credentialsNonExpired: true, enabled: true}
credentials: null
name: "123"
然后是算法,也就是认证实现
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication var1) throws AuthenticationException;
}
就是将认证信息作为参数,传入后通过authenticate函数认证
我看来看authenticate函数的实现,在ProviderManager类中
public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager, MessageSourceAware, InitializingBean {
// 省略
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass(); // 获取authentication的类型
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
Authentication result = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
Iterator var6 = this.getProviders().iterator(); // AuthenticationProvider的集合
while(var6.hasNext()) {
AuthenticationProvider provider = (AuthenticationProvider)var6.next();
// 当前provider是否支持认证这种类型的authentication
if (provider.supports(toTest)) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication attempt using " + provider.getClass().getName());
}
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication); // 认证
if (result != null) {
// 不为null则认证成功
this.copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
} catch (AccountStatusException var11) {
this.prepareException(var11, authentication);
throw var11;
} catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException var12) {
this.prepareException(var12, authentication);
throw var12;
} catch (AuthenticationException var13) {
lastException = var13;
}
}
}
// 都失败,抛给父类
if (result == null && this.parent != null) {
try {
result = this.parent.authenticate(authentication);
} catch (ProviderNotFoundException var9) {
} catch (AuthenticationException var10) {
lastException = var10;
}
}
if (result != null) {
// 清除敏感信息
if (this.eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication && result instanceof CredentialsContainer) {
((CredentialsContainer)result).eraseCredentials();
}
// publish success event,不知道中文怎么形容,下面失败一样
this.eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
return result;
} else {
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(this.messages.getMessage("ProviderManager.providerNotFound", new Object[]{toTest.getName()}, "No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
this.prepareException((AuthenticationException)lastException, authentication);
throw lastException;
}
}
// 省略
}
上面这些代码是总的处理流程,实际上单个处理流程在AuthenticationProvider
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication var1) throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> var1);
}
就认证和支持认证两个方法
这时候捋一捋
数据结构Authentication的继承类

算法AuthenticationProvider的继承类

一下一些知识是博客里看到的,就是AuthenticationProvider的继承类中
DaoAuthenticationProvider (extends AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider):最常用的认证方式,通过UserDetailsService对UserDetails认证
所以之后分析DaoAuthenticationProvider和AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider
- 从request中拿到username和password,存到一个
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(Authentication的接口实现类)对象中- 开始调用
AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.authenticate()方法- 拿到
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken的username- 调用
DaoAuthenticationProvider.retrieveUser(),用步骤3的username,调用UserDetailsService.loadUserByUsername()方法拿到User对象(UserDetails的接口实现类)- 检查步骤4中User对象的有效性(enabled,expired,locked)
- 调用
DaoAuthenticationProvider.additionalAuthenticationChecks(),比较UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken的password和UserDetails的password(都是encoded),一致则通过- 调用
AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.createSuccessAuthentication()修改和完善UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken信息,比如从UserDetails拿到的Authorities信息- 返回
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
User和UserDetails对象上面写代码的过程中接触过了
到这里其实我们已经大致理解了整个认证过程
然后我们需要知道的是什么时候调用这些流程
注解配置过程和过滤器链
首先可以直接从课程得到的是,过滤器链调用了上面的认证过程,说的细一点的话是org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter这个Filter
public class UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter {
// 省略
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
} else {
String username = this.obtainUsername(request);
String password = this.obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
this.setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
}
}
这个Filter调用了attemptAuthentication,它的父类AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter实现的doFilter方法中调用了这个方法,我们知道上面的认证流程在Filter执行doFilter方法时候进行的认证
然后是整个过滤器链和我们配置的注解的自己实现的类如何在Spring中整合起来的
这个部分太复杂了,已经超过我的理解和解释能力的范围,建议跟着这篇文章Spring Security(六)—SpringSecurityFilterChain加载流程深度解析看
之后我们就可以专注到这个过滤器链中
org.springframework.security.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter:(异步方式)提供了对securityContext和WebAsyncManager的集成,把SecurityContext设置到异步线程中,使其也能获取到用户上下文认证信息org.springframework.security.web.context.SecurityContextPersistenceFilter:(同步方式)在请求之前从SecurityContextRepository(默认实现是HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository)获取信息并填充SecurityContextHolder(如果没有,则创建一个新的ThreadLocal的SecurityContext),并在请求完成并清空SecurityContextHolder并更新SecurityContextRepositoryorg.springframework.security.web.header.HeaderWriterFilter:用来给http响应添加一些Header,比如X-Frame-Options,X-XSS-Protection*,X-Content-Type-Optionsorg.springframework.security.web.csrf.CsrfFilter:默认开启,用于防止csrf攻击的过滤器org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.LogoutFilter:处理注销的过滤器org.springframework.security.web.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter:表单提交了username和password,被封装成UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken对象进行一系列的认证,便是主要通过这个过滤器完成的,即调用AuthenticationManager.authenticate()org.springframework.security.web.authentication.ui.DefaultLoginPageGeneratingFilter:如果没有配置默认login,系统则会自动配置这个Filterorg.springframework.security.web.authentication.ui.DefaultLogoutPageGeneratingFilter:如果没有配置默认logout,系统会自动配置这个Filterorg.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationFilter:HTTP Basic Auth的过滤器org.springframework.security.web.savedrequest.RequestCacheAwareFilter:内部维护了一个RequestCache,用于缓存request请求org.springframework.security.web.servletapi.SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter:此过滤器对ServletRequest进行了一次包装,使得request具有更加丰富的APIorg.springframework.security.web.authentication.AnonymousAuthenticationFilter:匿名者身份的过滤器org.springframework.security.web.session.SessionManagementFilter:和session相关的过滤器,内部维护了一个SessionAuthenticationStrategy来执行任何与session相关的活动,处理Session维持攻击等org.springframework.security.web.access.ExceptionTranslationFilter:异常转换过滤器,这个过滤器本身不处理异常,而是将认证过程中出现的异常(AccessDeniedException and AuthenticationException)交给内部维护的一些类去处理org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterSecurityInterceptor:这个过滤器决定了访问特定路径应该具备的权限,这些受限的资源访需要什么权限或角色
整个过滤链的大致处理逻辑
当有一个非登陆请求过来的时候,会直接进到FilterSecurityInterceptor,验证是否登陆,如果登陆则放行请求;如果未登陆则抛出异常,被ExceptionTranslationFilter拦截后会重定向到登陆页面要求用户登陆。在此时如果用户填入用户名和密码点击登陆后,请求会被相应的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter、BasicAuthenticationFilter等Filter拦截,在Filter中进行用户登陆,如果用户登陆成功,则会把第一次的请求重定向到后面的Interceptor中继续判断是否可以访问REST API
0x02 RBAC授权Demo及授权过程原理分析
RBAC Demo实现思路
修改上面的认证逻辑,增加对admin用户和普通用户对权限区分
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
logger.info("登录用户名:" + username);
String password = passwordEncoder.encode("123456");
String role;
if (username.equals("admin")) {
role = "admin";
} else {
role = "normal";
}
logger.info("数据库密码是:" + password);
return new User(username, password, true, true, true, true,
AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList(role));
}
}
这里对用户名为admin的用户和普通用户的角色进行区分,返回不同的Authority,Authority就可以看作Role
然后修改对不通角色的路径配置
public class BrowserSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.formLogin()
.loginPage("/authentication/require")
.loginProcessingUrl("/authentication/form")
.successHandler(authenticationSuccessHandler)
.failureHandler(authenticationFailureHandler)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/authentication/require",
securityProperties.getBrowser().getLoginPage())
.permitAll()
.antMatchers("/user/1").hasAuthority("admin") // 增加的代码
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and().csrf().disable();
}
}
其实就增加了.antMatchers("/user/1").hasAuthority("admin")这一行,将/user/1和admin的Authority(Role)联系起来
然后分别用admin为用户名和不为admin用户名的用户登录,可以发现非admin用户名的用户登录后访问不了/user/1
授权过程流程分析
当我们有了上面对filter的描述,我们看描述也能猜到用来授权的是:org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterSecurityInterceptor:这个过滤器决定了访问特定路径应该具备的权限,这些受限的资源访需要什么权限或角色
public class FilterSecurityInterceptor extends AbstractSecurityInterceptor implements Filter {
// 省略
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain);
this.invoke(fi);
}
// 省略
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 校验请求不为空,且当前请求中已带有被校验过的标识,则放行请求
if (fi.getRequest() != null && fi.getRequest().getAttribute("__spring_security_filterSecurityInterceptor_filterApplied") != null && this.observeOncePerRequest) {
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
} else {
if (fi.getRequest() != null) {
fi.getRequest().setAttribute("__spring_security_filterSecurityInterceptor_filterApplied", Boolean.TRUE);
}
// 调用beforeInvocation去校验是否可以访问,详细之后分析
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try {
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
} finally {
super.finallyInvocation(token);
}
super.afterInvocation(token, (Object)null);
}
}
// 省略
}
我们知道Filter的doFilter方法中调用invoke方法,里面看起来比较有用的就是beforeInvocation方法了
看这个方法,我们从debug和源码两个方向分析,先看一张debug图
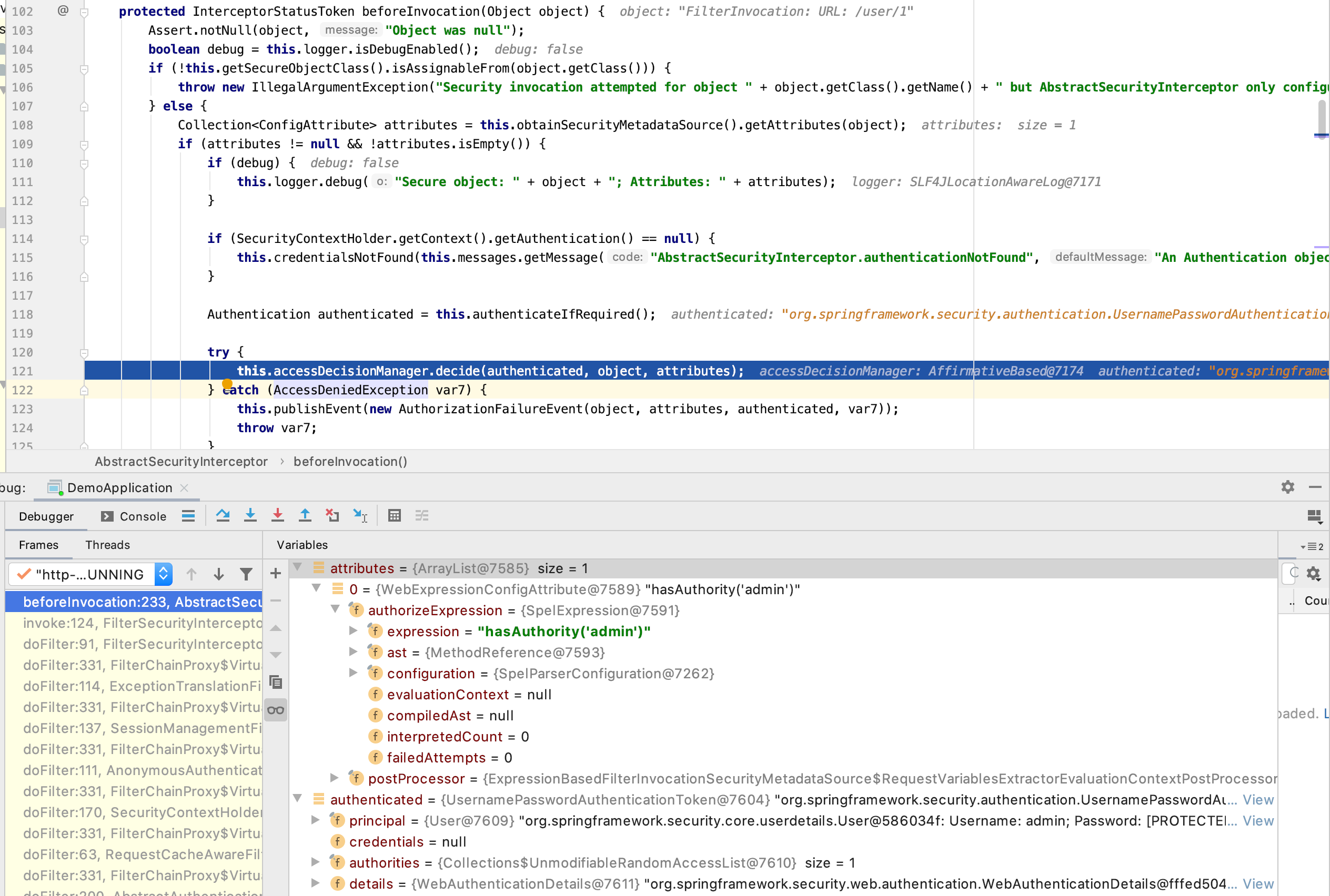
入参object是FilterInvocation,看debug的标识说明最重要的是URL,其实它包含Request、Response和Filter Chain
重要的一行是Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource().getAttributes(object)
通过debug返回值attributes我们可以得知这个函数是根据FilterInvocation,重要的是根据URL去获取,应该说获取的是授权的规则
接下来重要的一行是Authentication authenticated = this.authenticateIfRequired()
按我们之前对认证过程分析和debug显示的数据信息,我们知道Authentication是保存认证信息的,这里判断是否需要认证,需要就认证且返回认证信息,里面调用了authenticationManager.authenticate,也就是说这一步获取了认证结果
之后肯定就是授权了
也就是这一行 this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes),这里入参为认证结果、URL信息和授权规则,这就是这一步判断授权
之后的代码更新上下文、通知事件等就不重要了
然后我们将debug结果注释源码
public abstract class AbstractSecurityInterceptor implements InitializingBean, ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware {
// 省略
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object) {
Assert.notNull(object, "Object was null");
boolean debug = this.logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (!this.getSecureObjectClass().isAssignableFrom(object.getClass())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Security invocation attempted for object " + object.getClass().getName() + " but AbstractSecurityInterceptor only configured to support secure objects of type: " + this.getSecureObjectClass());
} else {
Collection<ConfigAttribute> attributes = this.obtainSecurityMetadataSource().getAttributes(object); // 获取授权规则
if (attributes != null && !attributes.isEmpty()) {
if (debug) {
this.logger.debug("Secure object: " + object + "; Attributes: " + attributes);
}
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
this.credentialsNotFound(this.messages.getMessage("AbstractSecurityInterceptor.authenticationNotFound", "An Authentication object was not found in the SecurityContext"), object, attributes);
}
Authentication authenticated = this.authenticateIfRequired(); // 获取认证结果
try {
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes); // 授权判断,出错则抛出异常
} catch (AccessDeniedException var7) {
this.publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated, var7));
throw var7;
}
// 省略
}
}
}
// 省略
}
总结
其实最难搞懂的部分,还是注解的配置和自定义的类怎么和在Spring流程中结合起来,其他知道结构,需要相应的功能分析对应的过滤器就可以
学习的时候看Response,默认增加了一些安全头部配置觉得很好,包括CSRF的默认配置
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
X-Frame-Options: DENY
不过其实虽然叫Security,但是基本还是认证和授权,对SQL、XSS这些还是没有除了头部以外的帮助,查了下资料过滤还是要自己实现
总体还是,难懂的是Spring框架,不是RBAC模型

